How to Beef Up an Old Laptop With Dial Up
Z7_3054ICK0KGTE30AQO5O3KA30N0
hp-concentra-wrapper-portlet
![]() Actions
Actions
HP Notebook PCs - Solve Internet or LAN Connection Issues When Using an Ethernet Cable to Connect to a Router or Modem (Windows Vista and XP)
A computer connected to the Internet using an Ethernet cable may occasionally lose its connection to the Internet. The computer may be connected directly to a cable service modem or DSL modem, or there may be a router between the computer and the modem. While some of the tasks listed below will resolve problems if the computer has lost its connection to other network computers, network storage devices, or network printers, this document primarily addresses a lost Internet connection.
note:Most of the troubleshooting steps below are quick and easy to perform. However, before you perform the Advanced Network Troubleshooting or try to download and install drivers or programs on your computer, try connecting another computer to the network to verify the problem is with the computer rather than a network issue.
Never connected
If the computer was never successfully connected to a network or the Internet, contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) for a wired LAN installation program and instructions, or see one of the following documents:
Wireless Connection
If the computer has lost a network or Internet connection on a wireless network, see one of the following documents:
Do this first
There are some simple troubleshooting steps you can perform before beginning the manual or advanced troubleshooting sections. These simple troubleshooting steps can solve many network and Internet connectivity issues.
Check network cabling connection
On most computers, there are light emitting diodes (LEDs) next to the physical connection where the Ethernet cable plugs into the computer. The LEDs glow or blink to indicate the current status of the network device. If the Ethernet connector on your computer does not have LEDs, you can look at the router to verify that the LEDs blink when the network cable is connected.
Use a Category 5 or Category 5e network cable (also referred to as a Cat-5 Ethernet cable) with RJ45 connectors on each end. A cable with smaller RJ11 connectors is used for connecting a dial-up modem to a telephone line.
RJ45 network connector RJ11 telephone connector

-
If the LEDs on the Ethernet connector blink as the computer is being used, the network card is connected properly to the network. To continue testing, go to Recycle power to reset the router and modem.
-
If the LEDs are not glowing, there may be a physical problem with the cable or connection. Do one or more of the following:
-
Unplug the Ethernet cable, blow out any dust from the connector, and re-plug the cable to establish a good connection.
-
Connect the computer to the network using a different Ethernet cable.
-
Connect the Ethernet cable directly from the computer to the modem to bypass all of the network wiring and the router.
-
If available, connect another computer to the network connector to determine if the problem is with the computer or the network.
-
Recycle power to reset the router and modem
The LEDs on the router and the modem should glow and blink when there is a connection between the computer, the network router, the modem, and the Internet. You should refer to the manufacturer's documentation for specific details. In general, one of the LEDs on the router glows steadily when there is a physical connection between the components, and a different LED blinks only when data is being transferred from the ISP. If the specific LEDs on the modem are not glowing or blinking, it indicates there is a problem with the Internet connection even if the LEDs on the router indicate connections between the computers and resources.
If the router cannot connect to the Internet, the browser displays a Cannot find server error message. To reset the router and the modem to their default condition, complete the following steps:
-
Turn off your modem.
-
Unplug the power, Ethernet and phone line/cable from the modem.
-
Turn off the router (if present in the network).
-
Unplug the power, Ethernet and phone line/cable (if using a modem router) from the router.
-
Shut down the computer.
-
Wait for 30 seconds for the power to dissipate from the devices.
-
Re-connect the Ethernet, phone line/cable and power to the modem.
-
Turn on the modem and wait for the modem to complete the startup process.
-
When all available LED lights are steady on the modem, connect the Ethernet, phone line/cable and power to the router.
-
Wait till the router completes the startup process and all available LED lights are steady.
-
Turn on the computer and attempt to reconnect to the Internet.
Manual Troubleshooting
You can manually troubleshoot Internet connection problems by completing the following tasks in the sequence they are listed.
Verify the network (NIC) is enabled
Reset the modem, router, and the computer. If the glowing LEDs indicate a good physical connection, but the computer cannot connect to the Internet or to a network resource, verify that the network device is enabled and has found the IP and DNS addresses automatically.
note:If connected to a private network, the computer may require the use of specific IP and DNS addresses. See the network administrator for the company's requirements.
For a PC with Vista
-
Click Start, type Network and Sharing in the search field, and then select Network and Sharing Center from the list.
-
Select Manage network connections in the left panel of the Network and Sharing Center window. The Network Connections window opens.
-
If the status of your Local Area Connection is disabled, right-click the Local Area Connection icon and select Enable. Otherwise, go to the next step.
-
Right-click the Local Area Connection icon and select Properties. The Local Area Connection Properties dialog box opens.
-
On the Networking tab, select the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) connection and click Properties. The Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box opens.
-
On the General tab, verify that both the Obtain an IP address automatically, and the Obtain DNS server address automatically options are selected, and then click OK to accept the values.
For a PC with XP
-
Click Start, Run, type ncpa.cpl in the Open field, and then click OK. The Network Connections window opens.
-
If the status of your Local Area Connection is disabled, right-click the Local Area Connection icon and select Enable. Otherwise, go to the next step.
-
Right-click the Local Area Connection icon and select Properties. The Local Area Connection Properties dialog box opens.
-
On the General tab, select the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) connection and click Properties. The Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box opens.
-
On the General tab, verify that both the Obtain an IP address automatically, and the Obtain DNS server address automatically options are selected, and then click OK to accept the values.
Remove Dial-Up connection setting from the browser
When a computer is connected to the Internet using a dial-up modem, the connection program creates an entry that forces the computer to try using the dial-up connection. When you attempt to use your browser, you may see a dial-up connection message or a Web page unavailable while offline error. To resolve these problems, you must disable the dial-up connection setting.
note:These steps work with Internet Explorer. The steps may be different for other Web browsers.
-
Open your browser, then click Tools, and Internet Options.
-
In the Internet Options dialog box, click the Connections tab.
-
Select the Never dial a connection option.
-
Click OK to save the settings.
Close and then re-start the browser to view a site on the web.
Examine the IP address to identify network problems
When computers are connected to the Internet or to a network, the communication is managed by using Internet Protocol Addresses (IP Address). An IP Address is a unique address that consists of four numbers separated by periods. For most cable and DSL devices, this number is assigned to the computer automatically by the ISP. If the ISP cannot assign the computer an IP Address, Windows assigns a default address or generates an error message.
Follow the steps below to find the IP Address, and then troubleshoot accordingly:
-
For Windows Vista, click Start, type cmd in the Search field, and press the Enter key to open the command window.
For Windows XP, click Start, Run, type cmd.exe in the Open field, and then click OK.
-
Type ipconfig /all at the command prompt, and then press the Enter key.
-
Look at the IP Address listed in Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection and take the indicated action.
Figure : Command window with IP address

-
If the IP Address is shown as Media Disconnected, Auto-configuration Address, or Fatal error: cannot read IP configuration, the NIC drivers are not installed or are corrupted.
Figure : Command window without IP address
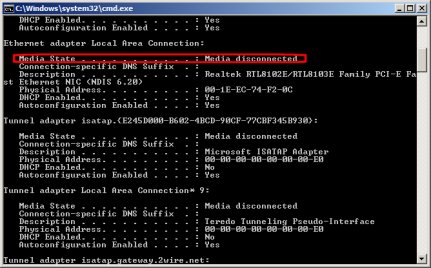
-
Check network status using the network icon
The network connection icon in the system tray indicates if the computer has a connection  or
or  , or does not have a connection
, or does not have a connection  or
or  , to the network or to a cable service modem or DSL modem. If there is no icon, either the icon display is turned off (in XP), or the network driver is missing or corrupted.
, to the network or to a cable service modem or DSL modem. If there is no icon, either the icon display is turned off (in XP), or the network driver is missing or corrupted.
To display the network connection icon, do the following:
For a PC with Vista
The network connection icon should display if any network (NIC) driver is installed. If the icon is not displayed, the driver is corrupted or missing. See, Download and install network driver.
For a PC with XP
-
Click Start, Run, type ncpa.cpl in the Open field, and then click OK. The Network Connections window opens.
-
Right-click the Local Area Connection icon, and select Properties. The Local Area Connection Properties dialog box opens.
-
On the General tab, verify that both the Show icon in notification area when connected, and the Notify me when this connection has limited or no connectivity options are selected, and then click OK to accept the values.
Figure : Local Area Connection Properties

The network connection icon will display in the system tray.
Download and install network driver
If the network connection icon is not displayed in the system tray, and the computer cannot connect to a network, you can install the required processor chipset and network interface card (NIC) drivers using one or more of the following installation options. HP recommends that you also update the BIOS, if available. As you review the options, click the Detailed Instructions link for more information.
Depending on the model, you should install the chipset drivers (Intel or Nvidia), NIC driver, or the Ethernet driver.
| Installation Options | Advantages |
| Run HP Support Assistant. | If the computer can connect to the Internet, HP Support Assistant can install the drivers for you. If you do not have a network connection, use one of the other Installation Options that do not require a network and Internet connection. |
| Update or reinstall original drivers using Device Manager. Detailed Instructions | Very quick and easy. Helpful if the driver is corrupted or was never installed. Will not help if the driver was uninstalled or deleted. Does not require a network and Internet connection. |
| Install the original drivers using Recovery Manager. Detailed Instructions | Available if the computer has the original HP image. Not available if the operating system was changed. Does not require a network and Internet connection. |
| Download and install the original or updated drivers from the HP web site. Detailed Instructions | Requires use of another computer with an Internet connection. The drivers must be downloaded from the Software & Driver downloads page on the HP web site, copied onto a disc or thumb drive, and then copied onto the computer that is missing the network driver. The drivers on the web site are the latest updated drivers. The latest BIOS and other drivers and software can also be downloaded. |
Install device drivers using the Device Manager
When networking hardware is not working correctly, Windows reports an error message in Device Manager. Use the following steps to refresh or reinstall the device drivers.
-
For Windows Vista, click Start and type Device Manager in the Search field. Select Device Manager when it becomes available in the Programs list. The Device Manager window opens.
For Windows XP, click Start, Run, type devmgmt.msc in the Open field, and then click OK. The Device Manager window opens.
-
If the Network adapters category is present in Device Manager skip to Step 4.
-
If the Network adapters category is not listed in Device Manager, check the following list and take the appropriate action:
-
Networking hardware is not installed. Install a new network PCMCIA card per the card manufacturers' suggestions. This does not apply to on-board networking hardware.
-
The network card is not seated fully into its socket. Remove and reseat the network PCMCIA card. This does not apply to on-board networking hardware.
-
-
If a network adapter is listed under the network adapter category, but has a yellow exclamation mark over its icon
 or
or  , do the following:
, do the following: -
In the Device Manager dialog box, highlight each listed driver one at a time and press the Delete key. When prompted, confirm that you wish to delete these drivers. Do not restart the computer.
-
In the Device Manager dialog box, click the Scan for hardware changes button (near the top). Windows will now scan your system for hardware and install default drivers for anything that requires drivers at this time.
-
Software drivers and supportive files may be missing or corrupted. Remove the device from Device Manager and reinstall the software by restarting the computer.
-
-
If the network adapter listed has a green adapter icon
 or
or  , the networking adapter is functioning correctly. Complete the following steps to verify the network hardware is working properly.
, the networking adapter is functioning correctly. Complete the following steps to verify the network hardware is working properly.-
Recheck the cable connections and replace any cables that have been bent or pinched, or that you suspect are bad.
-
Recycle the power to the modem, the router, and then restart the computer.
-
Check with the ISP's support service to verify that their service is operating. Most ISPs have a telephone support number. If an outage is occurring, an automated response about the ISP's system-wide service outages will probably play. In this case, wait until the service comes back.
-
Install original drivers using the Recovery Manager
If the computer cannot connect to the Internet but it does have the original HP image, you can use the HP Recovery Manager to install the original device drivers. The HP Recovery Manager can reinstall individual hardware drivers and software that shipped with the specific computer model. This installation option is not available if the operating system has been changed or if the Recovery drive (usually D:\Recovery) is corrupted or deleted.
To use the HP Recovery Manager to install the original device drivers, complete these steps.
For a PC with Windows Vista:
-
Click Start, type Recovery in the Search field, and select Recovery Manager, when it becomes available.
note:
Depending on the computer model, the HP Recovery Manager may be located in the Accessories folder or a different folder.
-
On the Recovery Manager main window, select the Advanced options.
-
On the Advanced options window, select the Hardware driver re-installation option, and then click Next.
-
When prompted, click Next to continue.
-
On the Select a driver to reinstall window, highlight the desired network device driver and click Next to begin the installation. Depending on the model, you should re-install the chipset drivers (Intel or Nvidia), the Network / Ethernet (NIC) driver, or the wireless LAN driver.

-
Repeat this action for the other hardware drivers to be re-installed.
-
If prompted after installing the drivers or network application, restart the computer.
For a PC with Windows XP:
-
Click Start, click All Programs, select System Recovery, and click Application & Driver Recovery.
-
Select an option to either Reinstall an Application or Reinstall a Driver shipped with the PC, and click Next.
-
Select the desired Application or Driver from the list, and click Next to begin the installation. Follow any additional instructions.
-
Restart the computer if prompted.
Install original or updated drivers from the HP web site
Sometimes the default drivers provided with Windows will not be up-to-date. If reinstalling the default drivers by using the Device Manager or the Recovery Manager does not correct the problem, you may need to reinstall the original and updated software drivers from the HP web site.
Since the computer is missing the network device drivers, it cannot connect to the Internet and you will need to use another computer to download the files. You will need a portable storage device, such as a CD or a thumb drive, to copy the files and then transfer them to the disconnected computer.
Download and install the latest driver using one of the following procedures:
-
Determine the exact product number for the computer. The product number is listed on the service tag on the bottom of the case. The model's series number near the display is not sufficient for locating the proper drivers.
-
Using a different computer that can connect to the Internet, go to the HP Software and Drivers web page to search for updated drivers.
-
Type the product number, and click the Next button.
-
Select Software & Driver Downloads.
-
Select your operating system, and then click Next.
-
Scroll through the list of drivers and locate the individual network device drivers. Depending on the model, you should download the chipset drivers (Intel or Nvidia), or Network / Ethernet (NIC) driver, or wireless LAN driver.
-
When you click on the name of the driver and the Download options and information page displays, be sure to read the Description to verify that it is the correct driver for your computer.
-
To download and save the driver, select Download, and then select Save when prompted.
Figure : Download and save options

caution:
Do not select Run because you do not want to install this software on this computer.
-
Navigate to a convenient location on the computer, such as the desktop, and save the file. Repeat this action for the other files to be downloaded.
-
When all the files are downloaded, copy the files to a portable storage device such as a CD or thumb drive.
-
Copy the files from the portable storage device to the computer that cannot connect to the network.
-
Double-click the copied files and install the required network drivers and software.
-
Restart the computer and verify the connection to the network and the Internet.
Also, update any Windows drivers and software using Microsoft's Windows Update feature.
Advanced Network Troubleshooting
If the computer cannot connect to the Internet after doing the quick network checks and the manual troubleshooting, you can complete one or more of the following advanced troubleshooting procedures. You may want to use a different computer to search the HP User support forums for similar network connection problems.
Troubleshoot IP protocol settings using the Command Prompt
The ISP should have provided all of the necessary settings and troubleshooting procedures for a proper cable or DSL connection. If the ISP does not provide technical support assistance, use the following steps to reset the network settings:
note:If you have the settings and troubleshooting procedures from the ISP, use them instead of the settings in this section.
-
For Windows Vista, click Start, type cmd in the Search field, and press in the Enter key to open the command window.
For Windows XP, click Start, Run, type cmd.exe in the Open field, and then click OK.
-
Type ipconfig /release at the command prompt and press the Enter key. The command prompt clears.
-
At the new command prompt, type the following text: ipconfig /renew and press the Enter key.
-
At the new command prompt, type the following text: netsh int ip reset c:\resetlog.txt and press Enter.
-
Close the Command window.
If the computer can connect to the Internet, you are done. If the computer still cannot connect to the Internet, continue using the following steps.
-
For Windows Vista, click Start, type Network and Sharing in the search field, and then select Network and Sharing Center from the list. Select Manage network connections in the left panel of the Network and Sharing Center window. The Network Connections window opens.
For Windows XP, click Start, Run, type ncpa.cpl in the Open field, and then click OK. The Network Connections window opens.
-
Right-click the Local Area Connection icon and select Properties. If prompted, allow the action to proceed. The Local Area Connection Properties dialog box opens.
-
Select the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) name that matches the Ethernet adapter name from the list of items for your connection. Do not remove the check mark next to the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) reference while selecting it. If multiple TCP/IP references are listed, select the one that contains the adapter name being used, such as TCP/IP -> 3Com Fast Ethernet Adapter.
note:
If there is no listing for Internet protocol (TCP/IP), this is the cause of the problem. Click Install, select Protocol, and then click Add. Select a TCP protocol from the list, such as Microsoft TCP IP, and then click OK to install the protocol. Restart the computer if prompted.
-
Select the Internet Protocol, and click Properties.
-
Select Obtain an IP address automatically and Obtain DNS server address automatically (if they are not already selected).
-
Click OK to close the TCP/IP Settings window, and then click OK to close the Local Area Connection Properties window.
-
Close all remaining windows, restart the computer, and try connecting to the Internet again.
Working with proxy servers and antivirus / firewall software
The Internet browser itself and other software, such as firewalls or proxy software, that are designed to protect the computer from on-line threats, can prevent the computer from connecting to the Internet. Follow the steps below to modify how the software on your computer works with the Internet:
Verify Proxy Server settings
Most home networks do not use a proxy server, however on a business network, you may want to check with the System Administrator for specific instructions.
-
For Windows Vista, click Start, type inetcpl.cpl in the Search field, and press the Enter key. The Internet Properties window opens.
For Windows XP, click Start, select Run, type inetcpl.cpl in the Open field, and click OK. The Internet Properties window opens.
-
In the Internet Properties window, select the Connections tab.
-
Click LAN Settings, and then select Automatically detect settings.
-
Remove the check marks to de-select the Use a proxy server for your LAN and Use automatic configuration script settings.
-
Click OK to accept the changed settings, and then OK to close the windows.
-
Try connecting to the Internet again. If the computer connects to the Internet, you are done. Otherwise, continue using these steps.
-
If proxy software is being used on a business network, disable it temporarily and try connecting to the Internet again. If the computer can connect to the network and the Internet, check with the System Administrator on a business network for specific instructions. Some common proxy software applications are:
-
WinProxy
-
WinGate
-
Microsoft Proxy Server
-
Netscape Proxy Server
-
Verify Firewall and Antivirus settings
HP recommends that all computers be equipped with some type of firewall and antivirus protection. However, these programs can block all access to the network or Internet if they are not set up correctly. You should only use one antivirus or firewall program at a time. Running two or more antivirus or firewall programs at the same time can make the computer operate slowly or prevent the computer from connecting to a network or the Internet. To review and change firewall and antivirus settings, do the following:
For Windows Vista, click Start, type security in the Search field, and then select Security Center from the listing. Follow the on-screen instructions to verify the security and firewall settings are on.
For Windows XP, click Start, Control Panel, and then Security Center. Follow the on-screen instructions to verify the security and firewall settings are on.
For testing purposes only - You can temporarily disable antivirus and firewall software to determine if one of these programs is preventing access to the Internet.
Using Windows Defender (Windows Vista only)
If you do not want to use any third-party programs, the Microsoft Windows Vista operating system includes Windows Defender, a native firewall and malicious software protection program. Windows Defender protects your computer against the latest threats, provides spyware detection and removal capabilities, and improves your computer safety while browsing the Internet.
To turn on the Windows Defender protection, follow these steps:
-
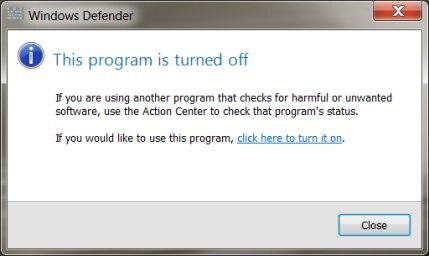
Click Start, type defender in the Search field, and then select Windows Defender from the list.
-
If Windows Defender is turned off, click click here to turn it on.
Figure : Defender turned off
-
Once Windows Defender is turned on, follow on-screen instructions for updating your computer to detect harmful software and prevent it from damaging your computer.
Figure : Check for updates on Windows Defender

Using Third-Party Programs
For most antivirus programs, right-click the application icon in the system tray, select the menu option to open the application control window. View the application's Help file for instructions on temporarily disabling the protection, and for configuring the firewall or antivirus settings. If the computer operates differently when the antivirus and firewall software is disabled, you have identified the cause of the problem.
If the computer can connect to the network or Internet after temporarily disabling your firewall software, refer to your ISP for the port numbers required to connect. Adjust your firewall software to allow these ports to stay open.
warning:Your computer is vulnerable to security threats when the firewall and antivirus software are disabled. When the testing is completed and the computer can access the Internet, re-enable the firewall and antivirus program and restart the computer.
Reset the default Winsock settings
The communication between the network components is managed by a set of built-in TCP/IP instructions. These instructions and address can become damaged or corrupted. If the computer was working but suddenly cannot connect to the network or the Internet, you can reset TCP/IP to its original default values by using a NetShell (netsh) command.
Eliminate many connection problems caused by third party software by resetting to the TCP/IP using the following steps.
-
For Windows Vista, click Start, type cmd in the Search field, and press in the Enter key to open the command window.
For Windows XP, click Start, Run, type cmd.exe in the Open field, and then click OK.
-
Type netsh winsock reset in the command window, and press the Enter key.
-
Allow the command to complete its operation.
-
Close the command window.
Using the NetShell command to rewrite two TCP/IP registry keys, provides the same results as reinstalling the TCP/IP protocol.
Source: https://support.hp.com/id-en/document/c00818622
0 Response to "How to Beef Up an Old Laptop With Dial Up"
Post a Comment